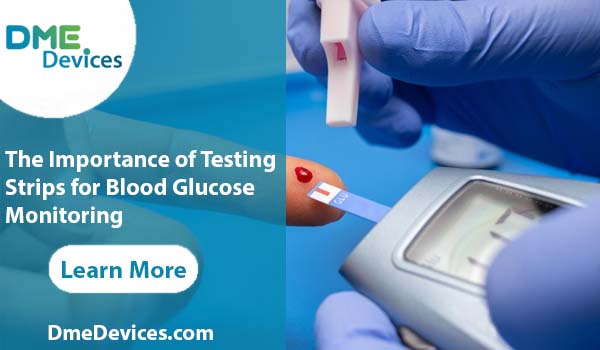
What are Testing Strips?
Testing strips are a crucial component of blood glucose meters, which are devices used by individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels. These strips are designed to work in conjunction with the meter, enabling it to measure the amount of glucose present in a small sample of blood. Without testing strips, a blood glucose meter would be rendered useless, as it relies on the chemical reactions that occur on the strip to provide accurate readings.
Each testing strip is a small, disposable piece of plastic or paper that contains a reaction area coated with enzymes and other chemicals. When a drop of blood is placed on this reaction area, the glucose in the blood reacts with these chemicals, producing an electrical current. The meter measures this electrical current and converts it into a numerical value that represents the blood glucose level.
Can You Use a Blood Glucose Meter Without Testing Strips?
No, it is not possible to use a blood glucose meter without testing strips. The testing strips are an essential part of the glucose monitoring process, as they contain the chemicals necessary for the meter to analyze the blood sample and provide an accurate reading. Without a testing strip, the meter would have no way to measure the glucose levels in the blood.
The Importance of Testing Strips
Testing strips are specifically calibrated to work with a particular brand and model of blood glucose meter. Each strip is coated with a unique combination of enzymes and chemicals that enable it to detect and measure glucose levels accurately. These strips are designed to interact with the meter’s specific technology, ensuring reliable and consistent results.
Using the wrong type of testing strip or attempting to use a meter without a strip can lead to inaccurate or unreliable readings, which can have serious consequences for individuals with diabetes. Incorrect blood sugar readings can lead to improper medication dosages, potentially causing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), both of which can be dangerous if left untreated.
Consequences of Using a Meter Without Testing Strips
Attempting to use a blood glucose meter without testing strips can have severe consequences for individuals with diabetes. Without a testing strip, the meter will be unable to analyze the blood sample and provide an accurate reading, potentially leading to the following issues:
- Incorrect medication dosages: Inaccurate blood glucose readings can result in incorrect insulin or medication dosages, which can cause dangerous blood sugar fluctuations.
- Hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia: Undetected low or high blood sugar levels can lead to serious complications, such as seizures, coma, or diabetic ketoacidosis (a life-threatening condition).
- Lack of monitoring: Without accurate blood glucose readings, individuals with diabetes may fail to recognize patterns or trends in their blood sugar levels, making it difficult to manage their condition effectively.
- Delayed treatment: Relying on inaccurate readings can delay the recognition of potential problems, leading to delayed treatment and potentially severe complications.
Proper Use of Blood Glucose Meters and Testing Strips
To ensure accurate blood glucose monitoring, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. This includes using only the testing strips specifically designed for your meter brand and model, following proper storage and handling guidelines for the strips, and adhering to the recommended testing procedures.
Expiration Dates and Storage Conditions
Testing strips have a limited shelf life and can become less effective or even unusable if they are exposed to extreme temperatures, humidity, or other environmental factors. It is crucial to check the expiration date on the strip vials and to store them according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Most testing strips are designed to be stored at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Exposing the strips to extreme heat, cold, or humidity can cause the chemicals on the strips to degrade, potentially leading to inaccurate readings.
Additionally, it is important to reseal the vial tightly after removing a strip to prevent exposure to air and moisture, which can also affect the strip’s performance.
Proper Coding and Calibration
Many blood glucose meters require coding or calibration with each new batch of testing strips to ensure accurate readings. This process involves entering a specific code or calibration number provided with the test strip vials into the meter. Failure to properly code or calibrate the meter with the appropriate test strip code can result in inaccurate blood glucose measurements.
The coding or calibration process is necessary because each batch of test strips may have slightly different chemical compositions or reaction characteristics. By entering the correct code, the meter can adjust its calculations to account for these variations and provide more accurate readings.
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when coding or calibrating the meter, as incorrect coding can lead to significant errors in blood glucose readings.
Proper Testing Technique
In addition to using the correct testing strips and following storage and coding guidelines, it is also important to follow the recommended testing technique for accurate results. This includes:
- Wash hands with warm water and soap before testing to remove any contaminants that could affect the reading.
- Using a fresh, sterile lancet for each test to ensure a clean blood sample.
- Apply the correct amount of blood to the test strip, as specified by the manufacturer.
- Properly timing the test and following any prompts or instructions from the meter.
- Disposing of used test strips and lancets safely to prevent potential exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
By following these guidelines and using the appropriate testing strips, individuals with diabetes can ensure reliable and accurate blood glucose monitoring, which is essential for effective diabetes management and preventing potential complications.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers, such as endocrinologists, diabetes educators, and certified diabetes care and education specialists, play a crucial role in ensuring that individuals with diabetes understand the importance of proper blood glucose monitoring and the correct use of testing strips.
Patient Education and Training
Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive education and training to individuals with diabetes on the proper use of their blood glucose meters and testing strips. This includes:
- Explain the importance of using the correct testing strips designed for their specific meter brand and model.
- Demonstrating the proper technique for obtaining a blood sample, applying it to the test strip, and interpreting the results.
- Educating patients on the storage and handling guidelines for testing strips, including expiration dates and environmental conditions that can affect their performance.
- Providing instructions on coding or calibrating the meter with each new batch of testing strips, if required.
- Emphasizing the potential consequences of using the meter without testing strips or with incorrect strips, such as inaccurate readings and potential medical complications.
Regular Follow-ups and Monitoring
Healthcare providers should schedule regular follow-up appointments with individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood glucose management and address any concerns or issues they may have with their testing supplies or techniques.
During these follow-ups, healthcare providers can:
- Review the patient’s blood glucose log and identify any patterns or trends that may require adjustments to their treatment plan.
- Assess the patient’s technique for using the blood glucose meter and testing strips and provide feedback or additional training if necessary.
- Ensure that the patient is using the correct testing strips and following proper storage and handling guidelines.
- Address any questions or concerns the patient may have about their testing supplies or the accuracy of their readings.
- Reinforce the importance of proper blood glucose monitoring and the consequences of inaccurate readings.
Collaboration with Pharmacists and Medical Supply Providers
Healthcare providers should also collaborate with pharmacists and medical supply providers such as DME Devices to ensure that individuals with diabetes have access to the appropriate testing strips for their specific blood glucose meter. This collaboration can include:
- Providing prescriptions or recommendations for the correct testing strip brand and model.
- Educating pharmacists and supply providers on the importance of dispensing the correct testing strips and the potential consequences of providing incorrect or incompatible strips.
- Coordinating with insurance providers to ensure proper coverage and reimbursement for testing supplies.
- Addressing any issues or concerns related to the availability or affordability of testing strips.
By working closely with individuals with diabetes, as well as pharmacists and medical supply providers, healthcare professionals can help ensure that proper blood glucose monitoring practices are followed, reducing the risk of inaccurate readings and potential complications.
In conclusion, using a blood glucose meter without testing strips is not possible and can lead to potentially dangerous consequences for individuals with diabetes. Proper use of testing strips, following manufacturer guidelines, maintaining recommended storage conditions, and receiving comprehensive education and support from healthcare providers are essential for accurate blood glucose monitoring and effective diabetes management.







Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required